Using Fyrite flue gas
analysers to measure Metabolic Rate
Patricia S. Bowne, Alverno College
Metabolic Rate is usually measured as the amount of
Oxygen used per time. It is standardized by weight as well, so large and small
animals can be compared. Therefore, a metabolic rate would usually be given as L O2 used per hour per kilogram of animal.
This means you need to get your subject's weight in kilograms (1 lb = 0.454
kg). Weigh your subject and enter her weight in the data table. Calculate her
weight in kilograms and enter that value.
To measure how
much O2 a human uses, we collect her exhaled air
and analyze it. The subject has to wear a nose plug and breathe through a
one-way valve setup; she inhales air from the room and exhales air through a
gas meter.
Collecting Exhaled Air
First, make sure
the mouthpiece and valves are clean. Then have your subject try them out; find
out which end she is inhaling from and which end she is exhaling out of.
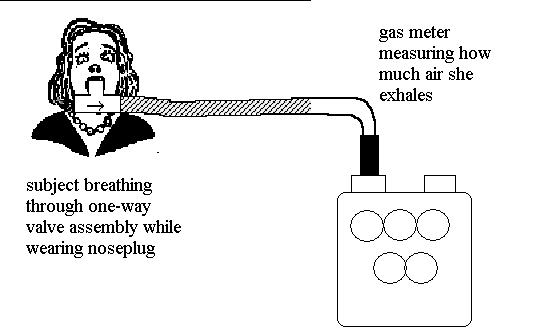
To get an accurate metabolic rate reading, let your subject relax for 5 minutes while breathing through the mouthpiece and wearing the nose plug. While she is doing this, the other group members should familiarize themselves with the gas meter.
The gas meter has many dials! Each dial tells you at the top how many CUBIC FEET of gas are measured by one revolution of the dial. Draw a picture of the face of your gas meter below, and mark IN PENCIL where all the hands are on the dials.
Now attach the hose from the gas meter to your subject's air output valve and have her breathe for 5 minutes. Draw the new positions of the hands on the gas meter dials.
How many CUBIC FEET of air did your subject exhale in 5 minutes?__________
While your subject
is breathing, follow the directions in the FYRITE TM instruction book to analyze the O2 level of the room air. It should be 21%,
or 21 mL O2/100 mL air.
You're not done with your subject yet! You want to know how much O2 your subject used during this experiment, so BEFORE UNHOOKING HER FROM THE APPARATUS, you need to take a sample of her exhalent. Do this by:
Detach the tube from the gas meter and make sure you can feel the air coming out of it as she exhales.
Use the Fyrite Oxygen meter to take a sample of her exhalent by putting the end of the sampling tube into the tube as she exhales. Pump the sample of exhaled air directly into the Fyrite as instructed in the manual, and measure the O2 content. Your subject is only done once you have the gas meter reading and the O2 reading!
How much O2 was in the air she EXHALED? ___________ mL O2/100 mL air exhaled
Now,
to get her metabolic rate you’re
going to take the amount of O2 that was in the air she inhaled and subtract
the
amount
that was in the air she exhaled. The difference will be the O2 she used
up.
Now you have a
value for the amount of O2 used, but it just applies to your experiment.
To compare it with the other students in the lab, you’ll need to calculate
some more standardized values. For instance, other groups may have collected
air for different lengths of time than you did. To compare your results with
theirs, you’ll need to calculate how much O2 your subject would use in an
hour. With this
value you can compare your subject to anybody else, no matter how long the
experiments were.
Your subject probably
doesn’t weigh the same as all the other subjects in the class. To compare
them, you should calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of subject. Enter
this in the data table under “metabolic intensity.” With this value, you
can compare your subject to anyone else, no matter how different their weights
are.
How much O2 would
she use per kilogram of her body weight per hour?
You never want
to do all that arithmetic again, do you?
Create
an Excel spreadsheet to do it for you, and use the spreadsheet
when you do your metabolic rate experiment.
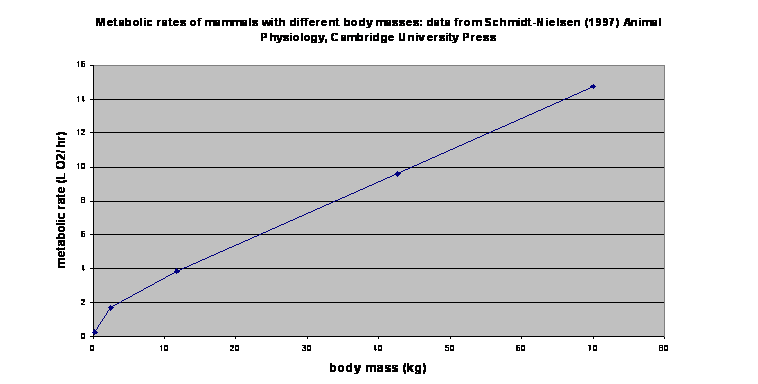
How does your
subject compare with the previous subjects on the data sheet? Here’s a graph of the O2 consumption of a set
of mammals; how does she compare with them? What do you think controls
metabolic rate in mammals?
Effect of Exercise
Now repeat your
metabolic rate measurement while the subject is exercising, to see how exercise
affects metabolic rate and minute ventilation. What happens?